Matrices are, rectangular block of numbers arranged in to rows and columns.
For example,
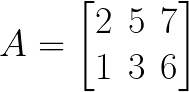
There are some unique terms that we should know when we are dealing with matrices.
Dimensions of Matrix
When we consider the above example it has two rows and three columns. So, the dimensions of matrix A is 2 x 3
Dimension of a matrix = Number of rows x Number of columns
Let’s find the dimension of the following matrices.
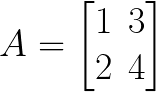
Dimension of A = 2 x 2
We called this one as two by two matrix.
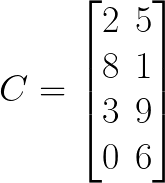
Dimension of C = 4 x 2
We called this one as four by two matrix.
Matrix Elements
Entries in a matrix are called elements of a matrix. Elements are defined by using rows and columns.
Let’s see an example.
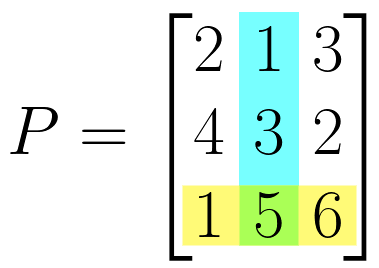
Equal Matrices
If matrix A = matrix B we can say that A and B are identical.
To A = B
01) The matrix A and B should be the same size.
02) Corresponding elements should be equal.
If,
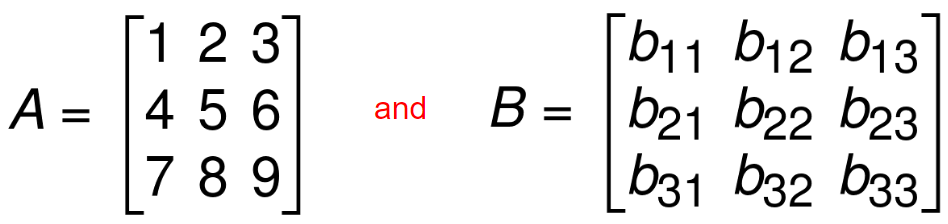
Then A = B means,
b11=1 , b12=2 , b13=3 , b21=4 , b22=5 , b23=6 , b31=7 , b32=8 , b33=9
Square Matrices
If the number of rows and columns of a matrix are same they are called Square Matrices.
Example:

2×2 , 3×3 , 4×4 , 5×5 , 6×6 , … matrices are examples for square matrices.
Zero Matrix
A matrix which consist of 0 s is called a Zero Matrix.
Examples:
Properties of a Zero Matrix
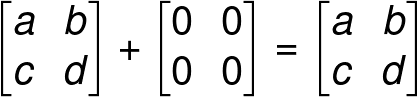
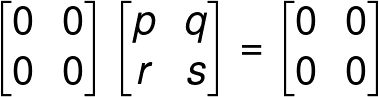
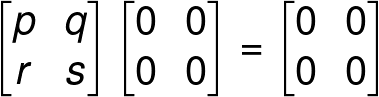
(Addition and multiplication of matrices will be describe later in this article.)
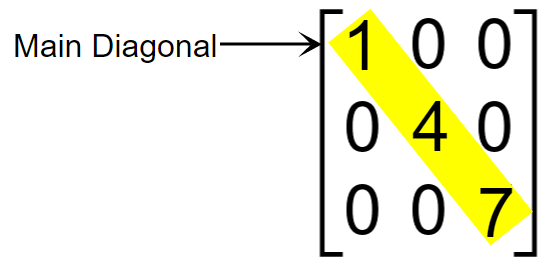
Diagonal Matrix
A diagonal matrix has zero entries all over the matrix except in the main diagonal. Diagonal matrices always come under square matrices.
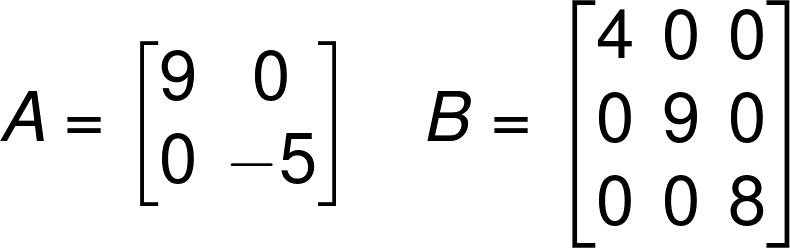
Identity Matrix
Identity Matrix is a matrix that has 1 s as the entries in the main diagonal.
We indicate identity matrices usually by the letter I
Examples:
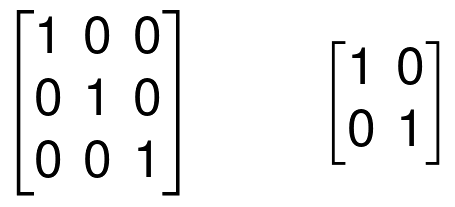
Properties of an Identity Matrix
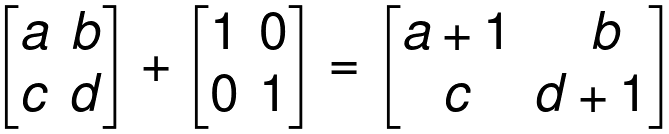
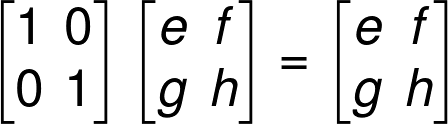
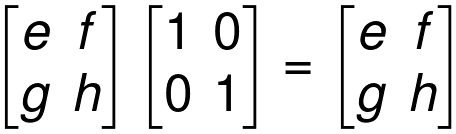
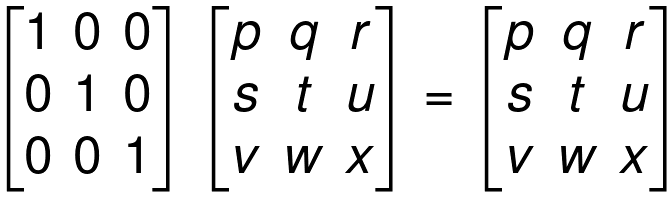
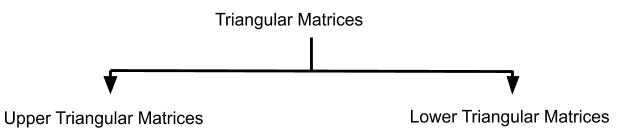
Triangular Matrices
The main diagonal divides a square matrix in to two triangles.
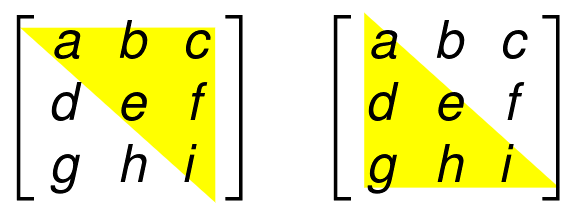
| A square matrix having zeros at all positions below the main diagonal. | A square matrix having zeros at all positions above the main diagonal. |

Transpose Matrix
Transpose of matrix A is denoted by AT
Two rows of AT are the columns of A.
The columns of AT are rows of A.
If A is m x n matrix then, AT is n x m matrix.

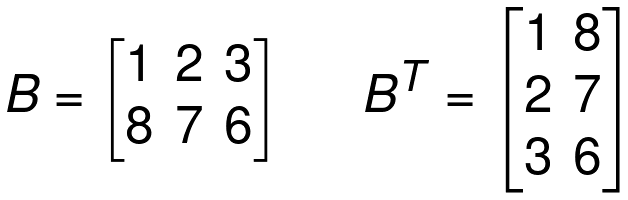
Symmetric Matrices
A is a square matrix.
If A = AT, A is Symmetric Matrix
Let’s see an example.
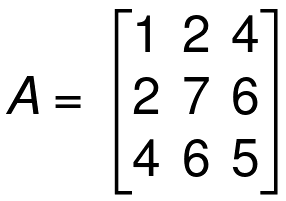
Now take the transpose of A.
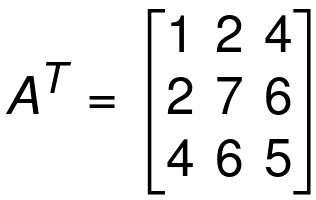
We can see that,
A = AT
So A is a Symmetric Matrix.
Before learning other definitions we have to learn about the addition and multiplication of matrices.
Addition of Matrices
If A and B are two matrices of the same size, we can get a matrix for A + B by adding the corresponding elements of A and B
Example 01
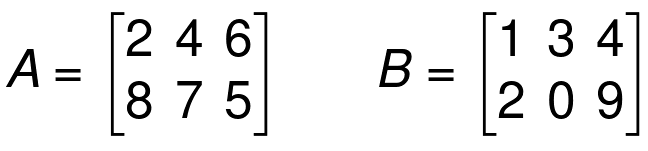
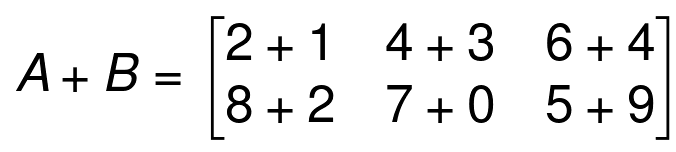
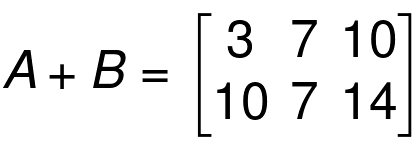
Example 02
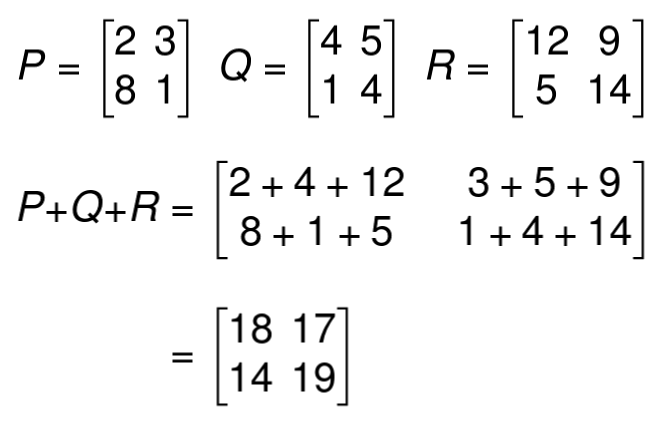
Multiplying Matrices
Multiplication of a Matrix by a Number
If A is a matrix and k is any real number, we can find kA by multiplying each element of matrix A by k.
Example:
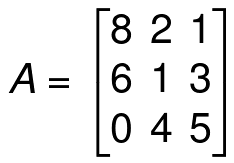
Find 4A,

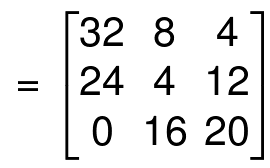
Multiplication of a Matrix by Another Matrix
It is easier to learn through an example.
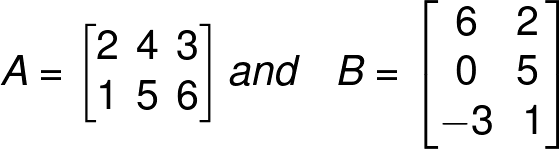
A is a 2 x 3 matrix, B is a 3 x 2 matrix.
AB will be,
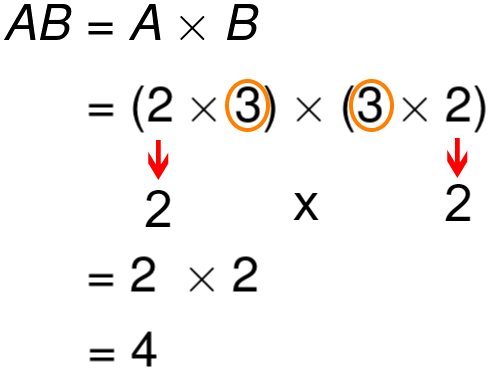
Let’s take,
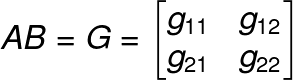
(Element in 1st row 1st column)
g11 = ( 2 x 6 ) + ( 4 x 0 ) + ( 3 x -3 ) ; Multiply the 1st row entries of A by 1st column entries of B.
= 12 + 0 – 9
= 3
(1st row 2nd column)
g12 = ( 2 x 2 ) + ( 4 x 5 ) + ( 3 x 1 )
= 4 + 20 + 3
= 27
(2nd row 1st column)
g21 = ( 1 x 6 ) + ( 5 x 0 ) + ( 6 x -3 )
= 6 + 0 – 18
= -12
(2nd row 2nd column)
g22 = ( 1 x 2 ) + ( 5 x 5 ) + ( 6 + 1 )
= 2 + 25 + 6
= 33
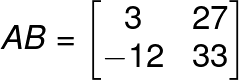
Let’s see another example.
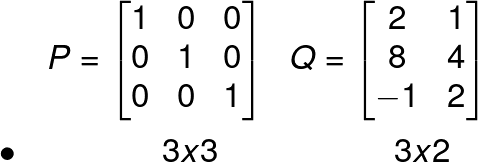
PQ will be 3 x 2 matrix,
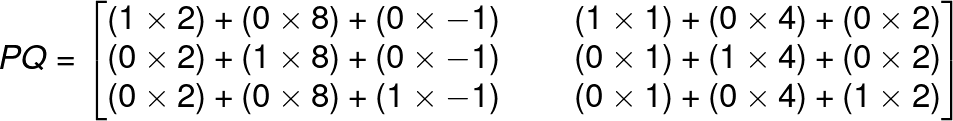
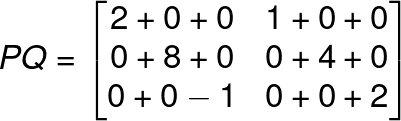
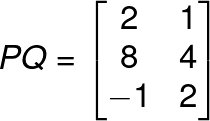
We can see that when we multiply a matrix by an identity matrix it will always give the same matrix.
Echelon Form of a Matrix
A matrix is said to be in Echelon form if,
a) All non-zero rows are above any rows of all zeros.
b) The leading coefficient of a nonzero row is always strictly to the right of the leading coefficient of the row above it.
c) The number of zeros proceeding the first nonzero element of a row increases as we proceed from row to row downwards.
Eg:
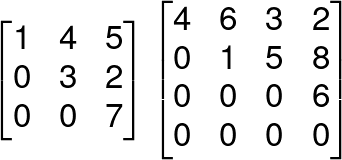
Row – Reduced Echelon Form of a Matrix
A matrix is said to be in row reduced echelon form when it satisfies the following properties.
a) The first nonzero entry in each row is 1.
b) Each successive row has its first nonzero entry in a later column.
c) All entries (above and) below the first nonzero entry of each row are zero.
d) All full rows of zeros are the final rows of the matrix.
Eg:

Reduce the following matrix to the echelon form.
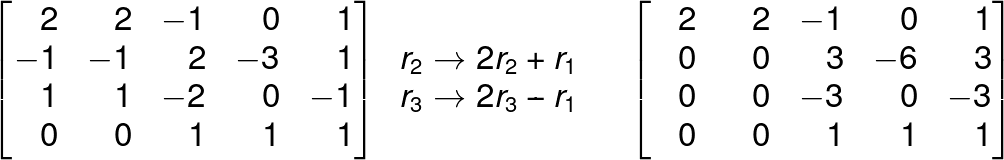
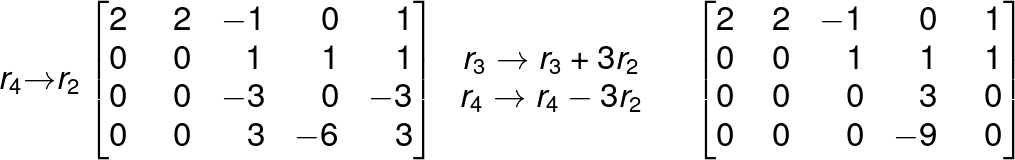
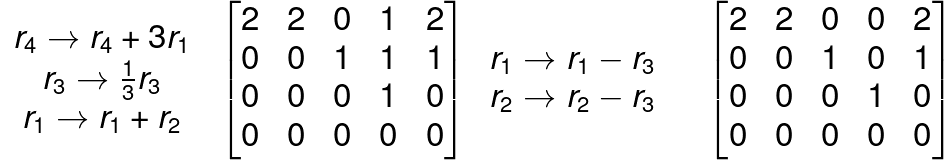
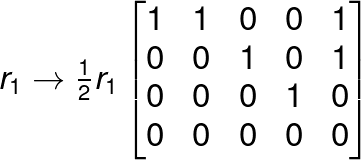
FAQ
What are matrices?
Matrices are, rectangular block of numbers arranged into rows and columns.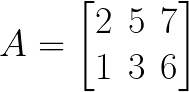
What are the dimensions of a matrix?
If we consider this image, the dimensions of this matrix A is 2 x 3.
The dimension of a matrix = Number of rows x number of columns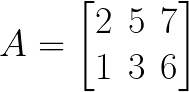
What are the Matrix Elements?
Entries in a matrix are called elements of a matrix. Elements are defined by using rows and columns.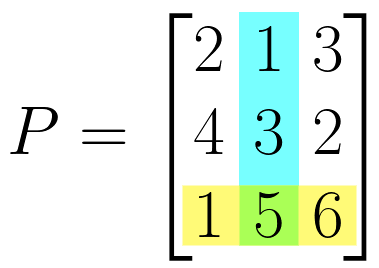
What are the Equal Matrices?
If matrix A = matrix B we can say that A and B are identical.
To A = B
What are the square matrices?
If the number of rows and columns of a matrix are same they are called Square Matrices.
What is a Zero Matrix?
A matrix which consist of 0 s is called a Zero Matrix.
What is a Diagonal Matrix?
A diagonal matrix has zero entries all over the matrix except in the main diagonal. Diagonal matrices always come under square matrices.
What is an Identity matrix?
Identity Matrix is a matrix that has 1 s as the entries in the main diagonal.
What are the Triangular Matrices?
The main diagonal divides a square matrix into two triangles.

What is the Echelon Form of a Matrix?
A matrix is said to be in Echelon form if,
a) All non-zero rows are above any rows of all zeros.
b) The leading coefficient of a nonzero row is always strictly to the right of the leading coefficient of the row above it.
c) The number of zeros proceeding the first nonzero element of a row increases as we proceed from row to row downwards.